What You Can Do with a Digital Media Degree
Tables of Contents

Digital media has evolved into a distinct discipline that influences — and is influenced by — rapid technological advances. Consumers demand fast, intuitive, useful ways to communicate and interact electronically.
Professionals in the digital media field work to ensure that individuals have access to and are adequately served by emerging technology in their everyday lives. We see the result of this work everywhere.
It is the convenience of a new smartphone app, the simplicity of a video conference call, the ease of finding a how-to video on YouTube. If you have read a news story, sought information on an internet search engine, listened to a podcast, watched an online video, or played a game on a digital device, you have experienced the fruits of the creativity and skill of a team of digital media professionals.
As the professional marketing and information industry world gravitated toward the digital space in the past decade-plus, the demand emerged for academic training in digital media. Today, a degree in digital media can serve as a stepping-off point for a career spent shaping the worlds of marketing, information sharing, and entertainment in the 21st century and beyond.
What Is Digital Media?
Digital media blends the electronic delivery of words and images, the proficiency of highly trained technicians, and the imagination of writers and other creative professionals. It is the newest iteration of marketing and information sharing.
Whereas creative energy once was the domain of print, radio, and TV advertising, the marketing world has used emerging communication technology to reinvent the brand-consumer relationship. Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Google ads, YouTube videos, Zoom online conferencing, and WordPress websites are just a few well-known examples of digital media entities that have shaped the culture in the past decade.

Digital media’s origins can be traced to the first half of the 19th century, when English researcher and mechanical engineer Charles Babbage and mathematician Ada Lovelace collaborated on calculations that are today considered the first rudimentary computer programming.
In 1945, American engineer Vannevar Bush seemed to presage the smartphone of today with his speculative essay “As We May Think” in The Atlantic magazine. In it, Bush envisioned a portable device that would allow users instantly to access detailed information about an endless array of topics.
Bush’s innovative ideas gave rise to a cultural vision of instant communication.
The advent of personal computers, followed by a wave of technological advances, such as the smartphone, email services, online shopping platforms, and high-speed internet connections, bring about new means of communication and commercial activity. Digital media proliferated in the form of increasingly powerful laptop computers and cellular phones toward the end of the 1990s, setting the stage for massive technological growth in the 21st century.
The Growth of Digital Media
The release of the first iPhone by Apple in 2007 sparked a new era in digital communication. As smartphone technology and cellular bandwidth improved, digital media professionals stepped in to give all those new users something to watch, listen to, read, and play.
By mid-2019, 81% of Americans owned a smartphone, according to mobile device research conducted by the Pew Research Center.
Smartphones enabled the growth of social media. Early platforms such as MySpace flourished briefly, but were left behind by social media behemoths Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat.
Google and Bing fulfilled Vannevar Bush’s vision of instant access to virtually limitless information. Amazon, Craigslist, and eBay drove the growth of e-commerce. YouTube’s growth gave rise to short-form video as a must-have tool for sales, marketing, entertainment, and information sharing.
The Future of Digital Media
The Pew Research Center queried 530 tech and communications experts for a 2019 nonscientific report that examined the future of digital media. Of the respondents, 72% agreed that digital media would contribute to a better life for people during the next five decades.
What does that mean? They believe digital media will contribute to longer lifespans, greater equity of wealth distribution, more quality leisure time, and a general improvement of human well-being.
Among the specific ways the experts believe digital media will evolve are:
- More individualized experiences, as content is personalized
- Deeper digital collaboration in business and in personal lives as connectivity improves
- Shifts in political power toward a broader base as access to information becomes more democratic
On the other hand, some experts warned that technological advances in digital media could lead to further social isolation, the potential for abuse if the means of communication are controlled by authoritarian regimes, and the potential for natural or human-made disasters to damage or destroy infrastructure.
No matter how it shakes out, digital media professionals will have a hand in determining the future course of electronic communication, entertainment, and information sharing.
Digital Media Skills
The skill set required to pursue a profession in digital media centers on technology. But communication skills, artistic ability, and creative imagination go hand in hand with tech engineering and programming.
Skills related to digital media include
- Communication
- Editing and writing
- Video production and editing
- Content management
- Marketing
- Technical computer knowledge
- Website design
- Photography
- Graphic design
Below is a breakdown of three interrelated areas of opportunity in digital media careers.
Web Developer Skills
Technology is the foundation of digital media, and web developers are the architects of the digital media infrastructure. A web developer must have a thorough knowledge of computer programming languages, as well as the platforms and applications used to create and manage websites.
Beyond that, a web developer must be able to concentrate for long periods spent writing and testing computer code. A creative mind helps web developers find new solutions when required. Communication skills also are vital, because web developers are called upon to interpret complex problems related to digital media.
Digital Content Skills
Digital content is the writing, video, visual graphics, and other assets published and shared on the internet. If web developers provide the framework and musculature of digital media, content creators — writers, editors, photographers, videographers — are its heart.
Digital content creators must have a thorough grasp of narrative storytelling. They must master grammar, spelling, style, voice, tone, and other elements of communication. They also must understand how and when to use different forms of media to achieve the desired effect on the target audience.
Visual Design Skills
Digital content is rarely served up in written form only. Visual elements, whether motion graphics or static images, attract attention and add depth to a written article. Beyond that, most infographics rely heavily on color, artistic appeal, and creative presentation of information to resonate with the audience.
A digital media career in visual design requires a measure of artistic talent, a deep knowledge of the use of color to convey meaning, an understanding of spatial relationships in presentations, and expertise in typography. It also helps to have excellent written and verbal skills, because visual designers collaborate often with other content creators and web developers.
Additional Visual Design Resources
Digital Media Specialist Skills and Career Path
Digital media is a broad field, with many specializations available for people with different skill sets. In general, a digital media specialist is a marketing or information industry professional who has chosen to specialize in a particular aspect of digital media.
Specializations are classified by media type and organizational mission. Some specialists go into marketing, advertising, or public relations. Others gravitate toward the news business.
Regardless of the mission, the various functions of digital media specialists remain similar.
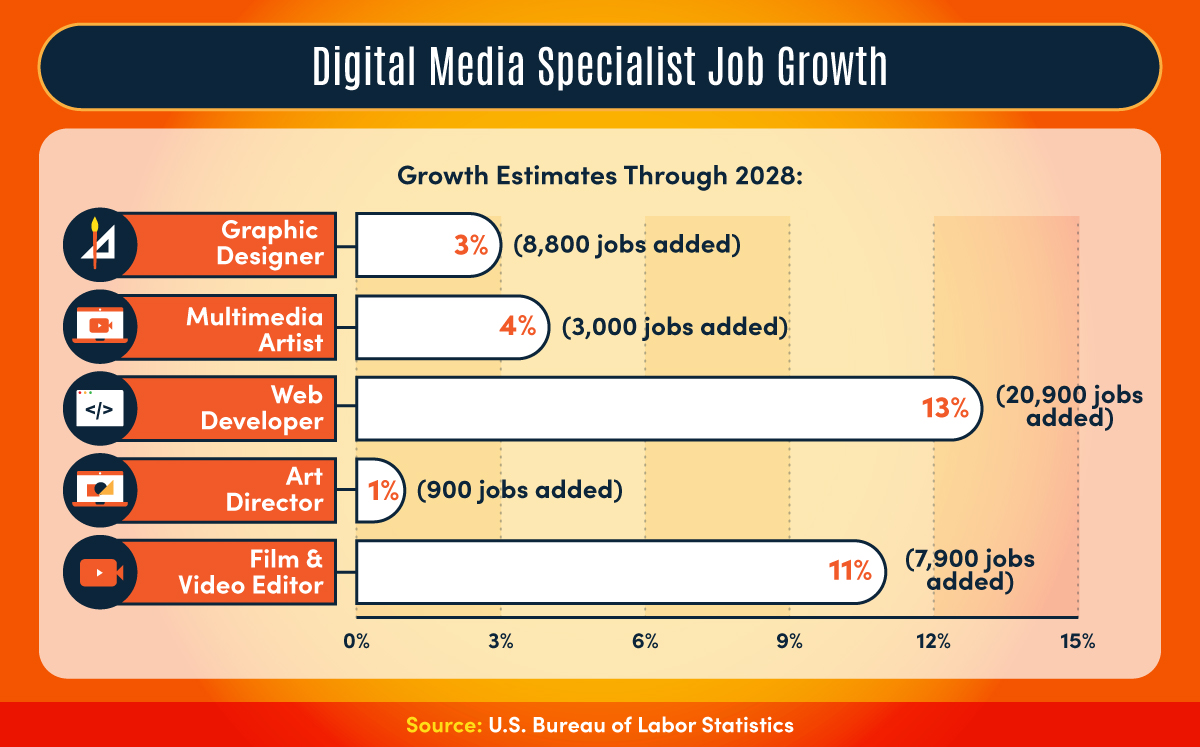
What Does a Digital Media Specialist Do?
Organizations need digital media specialists to produce and publish online content that attracts attention and delivers a message to a specific audience. Different types of digital media specialists work in tandem, often in a formal team structure.
For example, different projects and campaigns might each require the services of a specialist in graphic design, along with a copywriter, social media specialist, specialist in online advertising, email marketing specialist, and analyst to examine the effectiveness of the campaign. All of these specialists deploy tactics intended to support a specific marketing goal.
Digital Media Specialist Skill Set
The skill set required for a digital media specialist depends on the specialization.
A graphic designer will need to know how to produce visual content effectively, while a copywriter must understand how to fuse narrative storytelling and messaging. A web developer must know how to write code, while a video producer needs to have an understanding of script development and editing.
One quality most digital media specialists have in common is strong communication skills. No specialization serves every purpose in an organization, so smooth teamwork is essential.
Digital Media Specializations
There are many digital media specializations. Complicating matters for job seekers is the fact that not every organization uses the same title for positions that require similar skills.
For example, a video producer at one agency might develop, shoot, edit, and publish an entire film. Meanwhile, someone with the same title at a different organization might be responsible only for conceptualizing film ideas, writing the script, and overseeing the production, while others shoot and edit.
It is important to keep this in mind when considering the various digital media specializations, which include:
- Graphic designer
- Web developer
- Content manager
- Brand strategist
- Social media specialist
- Motion graphics designer
- User experience (UX) designer
- Paid search specialist
- Audio specialist
- Video editor
This is just a small selection of job titles found in the digital media industry. While each of the functions represented by the job titles is critical for effective messaging, some digital media specialists perform multiple roles — especially in smaller agencies.
Digital Media Creation: Additional Resources
Graphic Designer Skills and Career Path
Graphic designers are responsible for visual presentations that appear on digital publications. They often are referred to as graphic artists, for the simple reason that so much of what they do requires artistic skill.
Graphic designers can work their way up the organizational chain to become art directors, creative directors, marketing directors, chief creative officers, and other top positions.
What Does a Graphic Designer Do?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics’ (BLS) Occupational Outlook Handbook, a graphic designer creates “visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers.”
The job often requires collaboration with a copywriter on messaging concepts, an art director or creative director, a marketing strategist, and client representatives. During a given workday, graphic designers might be involved in the production of an infographic, social media post, digital ad, or visually oriented e-book.
They might meet with clients, work on a website layout, design a logo, or create an illustration to accompany a blog post. Anything visual falls under the purview of a graphic designer.
Graphic Designer Skill Set
Graphic designers must have artistic ability, as well as the ability to visualize a finished product based on the descriptions of clients or collaborators. It helps to have strong computer skills, especially with the many apps and programs used to create illustrations, graphics, charts, and designs.
Time management also is vital, especially in smaller agencies. Graphic designers often are asked to juggle multiple projects simultaneously, sometimes with overlapping deadlines.
Finally, a creative mind is a must. New ways to present visual elements in digital media are developed all the time. To remain successful, a graphic designer must be able to figure out how to implement new techniques and concepts.
Becoming a Graphic Designer
Most graphic designer positions require a bachelor’s degree in art, digital design, or a related field. The BLS says the National Association of Schools of Art and Design has accredited more than 360 postsecondary colleges, universities, and independent institutions to manage art and design programs.
Graphic designers often serve as interns with marketing or advertising agencies as they seek professional experience and build an attractive professional portfolio before they begin to seek full-time positions with agencies or in-house marketing teams.
Graphic Design: Additional Resources
Motion Graphics Designer Skills and Career Path
Motion graphics designers also might hold titles such as animator or multimedia artist. The basic function of the position is the same, no matter the title — to work with digital marketing strategists, social media specialists, video producers, and others to create compelling motion graphics.
A professional motion graphics designer often is expected to juggle multiple creative projects and meet multiple daily, weekly, or monthly deadlines. The designer works with an art director, a creative director, a client representative, or other stakeholders to produce short videos or elements of long films.
What Does a Motion Graphics Designer Do?
A professional motion graphics designer is an expert at creating moving images and visual effects. The designer might be asked to develop a project with specific creative elements, or to edit existing assets.
In a given week, a motion graphics designer might create a short animated video for a social media post, add motion to graphics on an existing video, or revise an element from an earlier project. The designer uses high-end computers, digital or hand-drawn storyboards, and specialized editing software to create illustrations that appear to move.
Motion Graphics Designer Skill Set
A motion graphics designer must have an artistic flair and a deep knowledge of modern creative editing and graphic design software. A high comfort level with using computers and learning new software and art techniques also is needed.
Communication ability is key. A motion graphics designer typically receives input from multiple stakeholders. Processing that input and translating it to a creative motion design takes skill.
Motion Graphics Designer Career Path
A motion graphics designer might earn a bachelor’s degree in art, design, or a related field, with an emphasis on animation and video editing. Computer programming knowledge also is required, as is a working knowledge of the various video platforms used by digital marketing teams.
An attractive and up-to-date portfolio is a must for designers who seek jobs with marketing or ad agencies. Motion graphics designers can work toward related management positions, such as video producer, art director, or creative director.
Motion Graphics: Additional Resources
UX Designer Skills and Career Path
A user experience designer, or UX designer, helps determine how people read, listen to, play, or watch a piece of content on digital media. If the web developer is responsible for the framework of a computer program or application, the UX designer is responsible for developing the concepts that the web developer makes possible through computer code.
Although similar to a user interface designer, or UI designer, a UX designer is not quite the same thing. The UX designer takes into consideration the entire ecosystem of the program or app. A UI designer works specifically on the details of how a user interacts with a digital experience. Think online forms, digital video players, and other interactive elements on a screen.
What Does a UX Designer Do?
A UX designer works closely with other members of the web development team to make sure that the digital product meets the original purpose, is intuitive for users, and contributes to any business goals related to the project or campaign.
Research is an important part of a UX designer’s duties. Primarily, this means delving into the psychographic motivations of users to make sure the product meets user expectations for ease of use and enjoyability. Surveys and focus groups contribute to deeper knowledge of user needs and motivations.
In addition, the designer must be able to recommend the most effective tools and programs available. Professional UX designers are always on the lookout for products that raise the industry standard or might present a new opportunity for their organization.
How Web Developers and UX Designers Work Together
A UX designer must have a working knowledge of web development to effectively communicate with the developers responsible for creating the framework of a program or app.
The UX designer will provide a vision for the structure of a website, including a representation of the website design known as a wireframe. The wireframe serves as a blueprint for the web developer to create a website or product, and includes all of the important information about the project.
During development, the UX designer and web developer will work closely to make sure the project stays on track.
Career Paths for UX Designers
UX designers earn a bachelor’s degree in project management, programming, or another computer-related field. They might serve internships with marketing or ad agencies while in college.
One way for UX designers to stand out is to develop an expertise in user experience on multiple platforms: desktop, mobile, gaming, and more.
UX Design: Additional Resources
What’s Next in Digital Media?
Digital media is a fast-moving, fast-changing discipline. Technological advances happen all the time. This year’s hot new gadget or social media platform might be forgotten by this time next year.
The big tech companies — Apple, Google, Amazon, Facebook, Samsung, Sony, and others — constantly seek to gain a competitive edge. It is incumbent on digital media professionals to keep up to date on new developments in the industry.
Even now, relatively new technology such as augmented reality, virtual reality, and the implementation of artificial intelligence is shaping the digital media industry. Annual conferences and expositions such as the Electronic Entertainment Expo (E3) in Las Vegas, Social Media Marketing World in San Diego, and the Cannes Lions International Festival of Creativity offer big companies the chance to show off new tech — and the chance for aspiring digital media professionals to keep up with what’s next.
Sources
Adobe blog, “Hiring Trends in UX Design”
The Balance, “Important Digital Media Skills that Employers Value”
Hubspot, “The Who, What, Why & How of Digital Marketing”
Sprout Social, “41 Must-Have Digital Marketing Tools to Help You Grow”
Statista, “Film Industry: Statistics and Facts”
Study International, “Finding Opportunity in the Digital Age”
Be Brave
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.

